The Future of Biometric Security: Beyond Passwords
6 min read
04 Sep 2024
In an increasingly digital world, the traditional password is facing numerous challenges: it's difficult to remember, susceptible to hacking, and often inadequate for ensuring robust security. As a result, biometric security technologies are emerging as the next frontier in safeguarding sensitive information and digital identities.
Evolution of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication utilizes unique biological characteristics such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, and even behavioral traits like voice or typing patterns to verify an individual's identity. Unlike passwords, which can be forgotten, shared, or stolen, biometric data offers a more secure and convenient method of authentication.
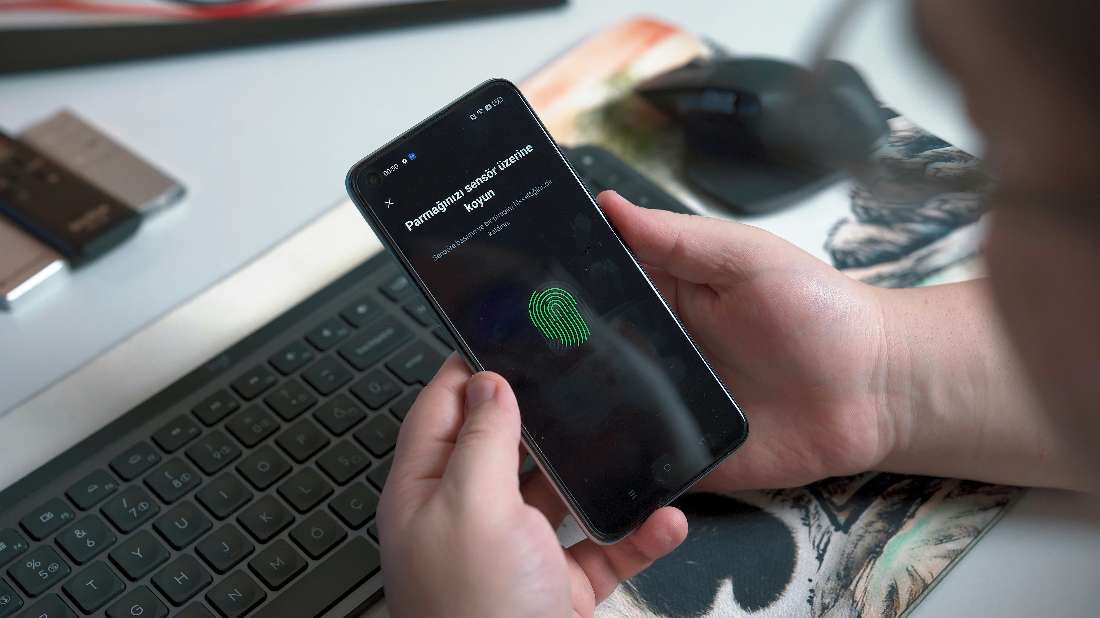

Advancements in Biometric Technology
Recent advancements in biometric technology have significantly enhanced accuracy, speed, and reliability. High-resolution sensors and sophisticated algorithms enable precise capturing and analysis of biometric data, minimizing false positives and negatives. This makes biometric authentication not only secure but also user-friendly.
Applications Across Industries
Biometric security is already widely adopted in various industries. In banking and finance, fingerprint or facial recognition is used to authorize transactions securely. In healthcare, biometrics ensure only authorized personnel access sensitive patient records. Governments use biometrics for border control and identification purposes, enhancing security and efficiency.
Addressing Privacy Concerns
Despite its benefits, biometric security raises concerns about privacy and data protection. Biometric data, once compromised, cannot be changed like a password. Therefore, stringent regulations and encryption standards are essential to safeguard biometric information and mitigate potential risks.
Future Trends and Innovations
Looking ahead, biometric security is poised for further evolution. Advancements in AI and machine learning will enable systems to continuously improve accuracy and adaptability. Multi-modal biometrics, combining different biometric identifiers, will enhance security further by reducing vulnerability to spoofing attacks.
Challenges and Considerations
As biometric technology becomes more prevalent, interoperability among different systems and standardization of protocols will be crucial. Additionally, addressing ethical considerations such as consent, transparency, and inclusivity in biometric deployments will be essential for widespread acceptance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biometric security represents a significant advancement in authentication technology, offering a more secure, convenient, and reliable alternative to traditional passwords. While challenges remain, ongoing research and innovation promise to make biometric authentication even more integral to our digital lives, ensuring enhanced protection of personal and sensitive information.
Biometric security is not just a futuristic concept but a rapidly evolving reality that is reshaping the landscape of digital security. As businesses, governments, and individuals embrace biometrics, the days of passwords may soon be numbered.
More Articles

The Next Frontier: AI & ML's Role in Climate Change Mitigation
7 min read | 07 Aug 2024

Unraveling the Black Box: Understanding Transparency in AI & ML
5 min read | 06 Aug 2024

AI Odyssey: Journeying through the Realm of Machine Learning
7 min read | 05 Aug 2024

The Quantum Leap: AI & ML Redefining Possibilities
4 min read | 04 Aug 2024
More Articles

Smart Fabrics: The Integration of Technology in Textiles
7 min read | 06 Sep 2024

AI in Drug Discovery: Accelerating Pharmaceutical Research
5 min read | 05 Sep 2024
Synthetic Biology: Engineering Life at the Molecular Level
7 min read | 04 Sep 2024

Haptic Technology: Touch Feedback in Virtual Environments
4 min read | 03 Sep 2024
